An mRNA or messenger RNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that uses a copy of messenger RNA to produce an immune response. This is achieved through mRNA transfection, the process of introducing mRNA into a living cell. In order to learn how mRNA vaccines work, we need to understand where mRNA comes from.
How mRNA is formed?
Nucleic acids are the main information-carrying molecules of the cell. They direct the process of protein synthesis and determine the inherited characteristics of every organism. Nucleic acids include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid).
What is DNA?
DNA is the genetic/hereditary information that parents pass down to their offspring. This genetic information codes for everything that is found in an organism. DNA is found within the nucleus and has the ability to make copies of itself which allows for individual cells to reproduce. It also has the ability to direct RNA synthesis and produce RNA. DNA is a double-stranded molecule while RNA is single-stranded.
Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis, also known as gene synthesis, is the production of proteins in the cells of all living things. This consists of two processes: transcription and translation.
Transcription
The process of synthesizing RNA from DNA is known as transcription. Transcription occurs within the nucleus of the cell. During the transcription, genetic instructions are transferred from DNA to mRNA.
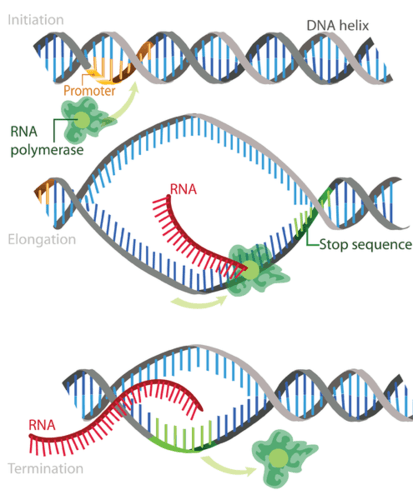
Transcription occurs in three steps namely initiation, elongation, and termination. Once the mRNA is processed from DNA, it can then leave the nucleus through the nuclear pores and enter into a ribosome in the cytoplasm.
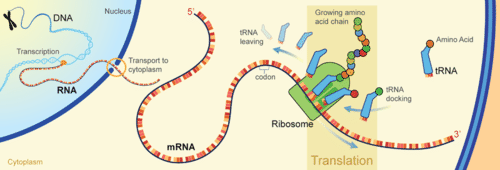
Translation
Translation occurs at the ribosome which consists of rRNA (ribosomal ribonucleic acid) and proteins. During translation, the instructions in mRNA are read and then tRNA (transfer RNA) brings the correct sequence of amino acids to the ribosome. Then, the rRNA helps bonds form between amino acids, producing a polypeptide chain. Once synthesized, the polypeptide chain may undergo additional processing to form the finished protein.[1]
How traditional vaccines work?
A vaccine is a type of medicine that is designed to help train our body’s immune system to fight a disease that it has never come into contact with before. Vaccines are designed to prevent a disease rather than treating a disease once you have caught it. They prompt our immune system to respond as it would have on its first reaction to the actual pathogen.[2]
Ordinary vaccines use inactivated or weakened parts of a particular organism (antigen) that triggers an immune response within the body. The process involved in making such vaccines requires various chemicals and cell cultures. As a result, their manufacturing process is time-consuming and can get contaminated. This is where mRNA vaccines come in.
How do mRNA vaccines work?
mRNA vaccines contain the blueprint for producing antigens rather than the antigen itself. They instruct the body to make the offending proteins. These are the proteins that wrap around the viral or cancer cells. Delivery of mRNA is achieved by a co-formulation of the molecule into lipid nanoparticles which protect the RNA strands and helps their absorption into the cells.
Once inside the immune cells, mRNA vaccines prompt cells to build the foreign protein that would normally be produced by a pathogen or by a cancer cell. These protein molecules stimulate an adaptive immune response which teaches the body to identify and destroy the corresponding pathogen or cancer cells.
The biggest advantage of the mRNA vaccine is that it can tell our cells to make whatever protein we require. This includes the antigens for many other diseases besides Covid-19. They are genetically safe because mRNA can’t go back into the nucleus and accidentally insert genes into our DNA.
How COVID-19 mRNA vaccines work?
COVID-19 mRNA vaccines like the ones made by BioNTech and Moderna work by first figuring out what protein they want, a spike protein on the coat around a SARS-CoV-2 virus. Then they look at the sequence of amino acids that makes this protein. From this, they derive the precise instructions that mRNA must give. Their manufacturing process is relatively faster than traditional vaccines that is why it took less than a year to make COVID-19 vaccines.
References
1. Protein synthesis
2. How do vaccines work?