A mirror at Goddard Space Flight Center
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) which is currently under development is the successor of Hubble Space Telescope.
It is also known as the Next Generation Space Telescope is named after the NASA administrator James E.Webb who played an important role in Apollo program. The telescope is a joint project by NASA, European Space Agency and Canadian Space Agency.
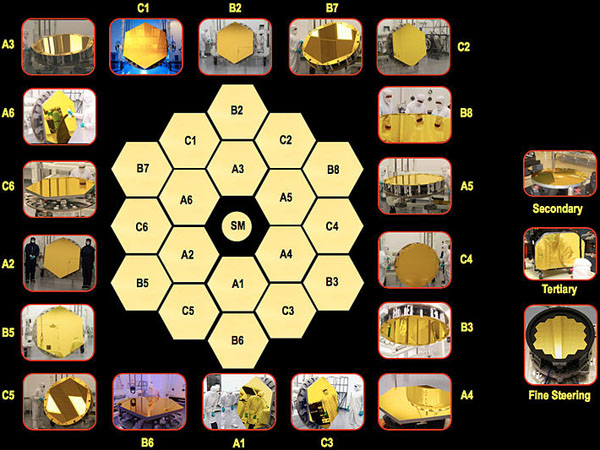
The James Webb Space Telescope comprises of 21 mirrors which includes primary mirror segments, secondary mirror, tertiary mirror and fine steering mirror.
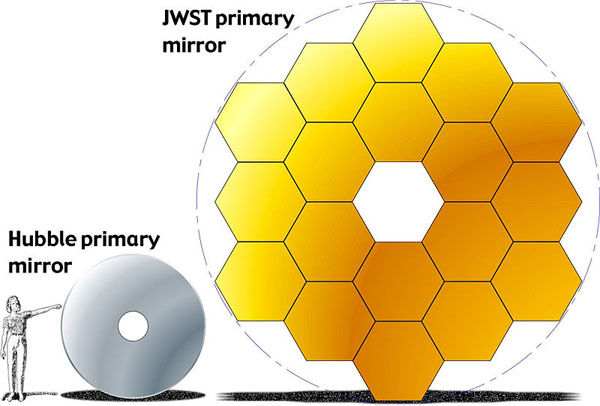
The primary mirror has a diameter of 6.5m and is a gold coated berylllium reflector. The primary mirror has 18 hexagonal mirror segments that provides a large collecting area on the telescope.
Unlike the primary mirror, the secondary mirror is a round one. It is convex and it bulges towards the light source.
The secondary mirror has the finest surface finish and it wont change its design under extreme cold temperatures. The secondary mirror is mounted on a tripod above the primary mirror.
The tertiary mirror and fine steering mirror are located inside an assembly near the center of primary mirror. All the mirrors used in the telescope are made up of beryllium which is suited for stiffness, light weight and can withstand cryogenic temperatures.
Beryllium does not efficiently reflect infrared light, so it is coated with gold to improve its reflecting properties. The James Webb Space Telescope once launched into space, it will start providing images of distant planets and very first galaxies formed in the universe.
Related posts: