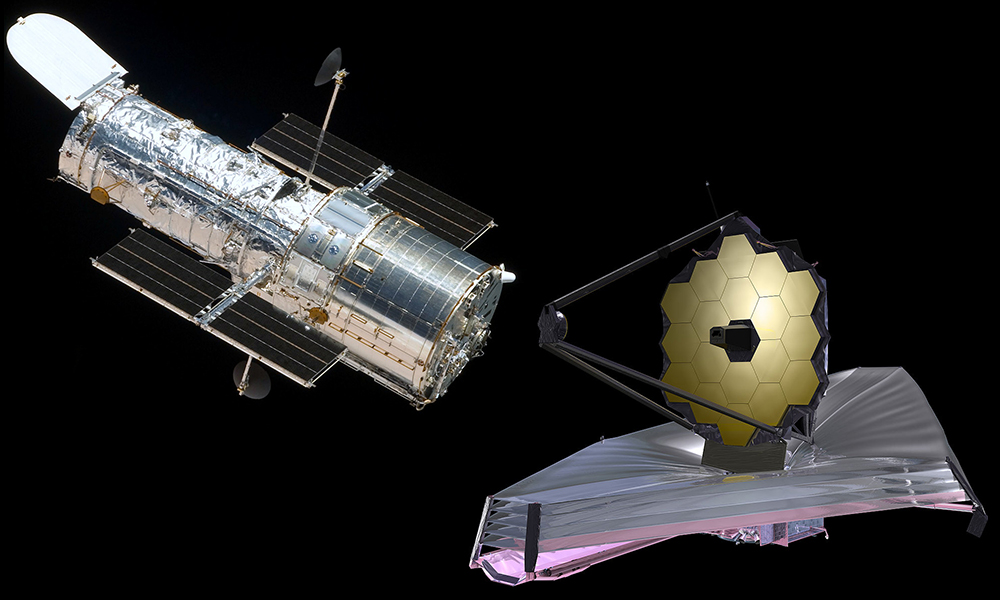
Hubble Space Telescope (HST) has been one of the greatest achievements of mankind which have opened our eyes to the vast universe. In order to expand our visible universe and view much longer wavelengths, Hubble Space Telescope needs a successor, which is the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).
As our universe is continuously expanding, more distant objects are highly redshifted and their light is pushed from the ultraviolet and optical spectrum to the near-infrared spectrum. So we need an infrared telescope to view into the distant past. And the James Webb Space Telescope is designed just for that.
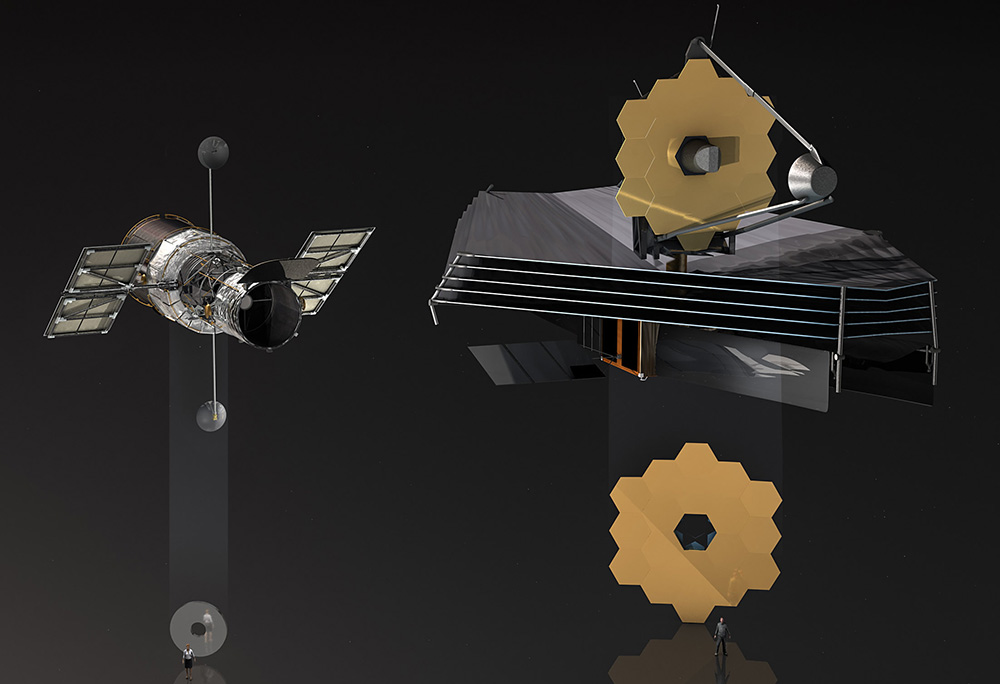

| Hubble Space Telescope | James Webb Space Telescope |
| Named after: Edwin Powell Hubble | James Edwin Webb |
| Launch date: April 24, 1990 | March 30, 2021 (Planned) |
| Launch site: Kennedy Space Center (LC-39B) | Guiana Space Centre (Kourou ELA-3) |
| Rocket: Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31) | Ariane 5 ECA |
| Launch mass: 10,886 kg (about 24,000 lb) | 6,500 kg (14,300 lb) |
| Dimensions: 13.2 m × 4.2 m (43.3 ft × 13.8 ft) | 21.197 m x 14.162 m (69.5 ft x 46.5 ft) (sunshield) |
| Power: 2,800 watts | 2,000 watts |
| Orbital reference system: Geocentric | Sun-Earth \(L^2\) |
| Orbital regime: Low Earth orbit | Halo orbit |
| Perigee altitude: 537.0 km (333.7 mi) | 374,000 km (232,000 mi) |
| Apogee altitude: 540.9 km (336.1 mi) | 1,500,000 km (930,000 mi) |
| Orbital period: 95.42 minutes | 6 months |
| Mission duration: Elapsed: 30 years and counting | 5 years (design), 10 years (goal) |
| Manufacturers: Lockheed (spacecraft), Perkin-Elmer (optics) |
Northrop Grumman, Ball Aerospace (Mirrors) |
| Operators: National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), European Space Agency (ESA), Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI). |
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), European Space Agency (ESA), Canadian Space Agency (CSA), Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI). |
| Telescope type: Ritchey–Chrétien telescope | Korsch telescope |
| Primary mirror diameter: 2.4m (7.9 ft) | 6.5 m (21.3 ft) |
| Focal length: 57.6 m (189 ft) | 131.4 m (431 ft) |
| Collecting area: 4.525 \(m^2\) (48.7 sq ft) | 25.4 \(m^2\) (273 sq ft) |
| Wavelength: 0.1 to 0.8 μms (ultraviolet and visible spectrum), 0.8 to 2.5 microns (near-infrared) |
0.6 – 28.5 μm (infrared), Visible spectrum (red and up to the yellow part of the visible spectrum) |
| Instruments: ACS Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3), Cosmic Origins Spectrograph (COS), Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS), Fine Guidance Sensor (FGS) |
Near InfraRed Camera (NIRCam), Near InfraRed Spectrograph (NIRSpec), Mid-InfraRed Instrument (MIRI), Fine Guidance Sensor and Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (FGS/NIRISS) |
The primary mirror of James Webb Space Telescope is a gold-coated beryllium reflector. The primary mirror has 18 hexagonal mirror segments that provide a large collecting area on the telescope.
Unlike the primary mirror, the secondary mirror is round one. It is convex and it bulges towards the light source. The secondary mirror has the finest surface finish and it won’t change its design under extremely cold temperatures. The secondary mirror is mounted on a tripod above the primary mirror.
References:
Hubble Space Telescope
James Webb Space Telescope