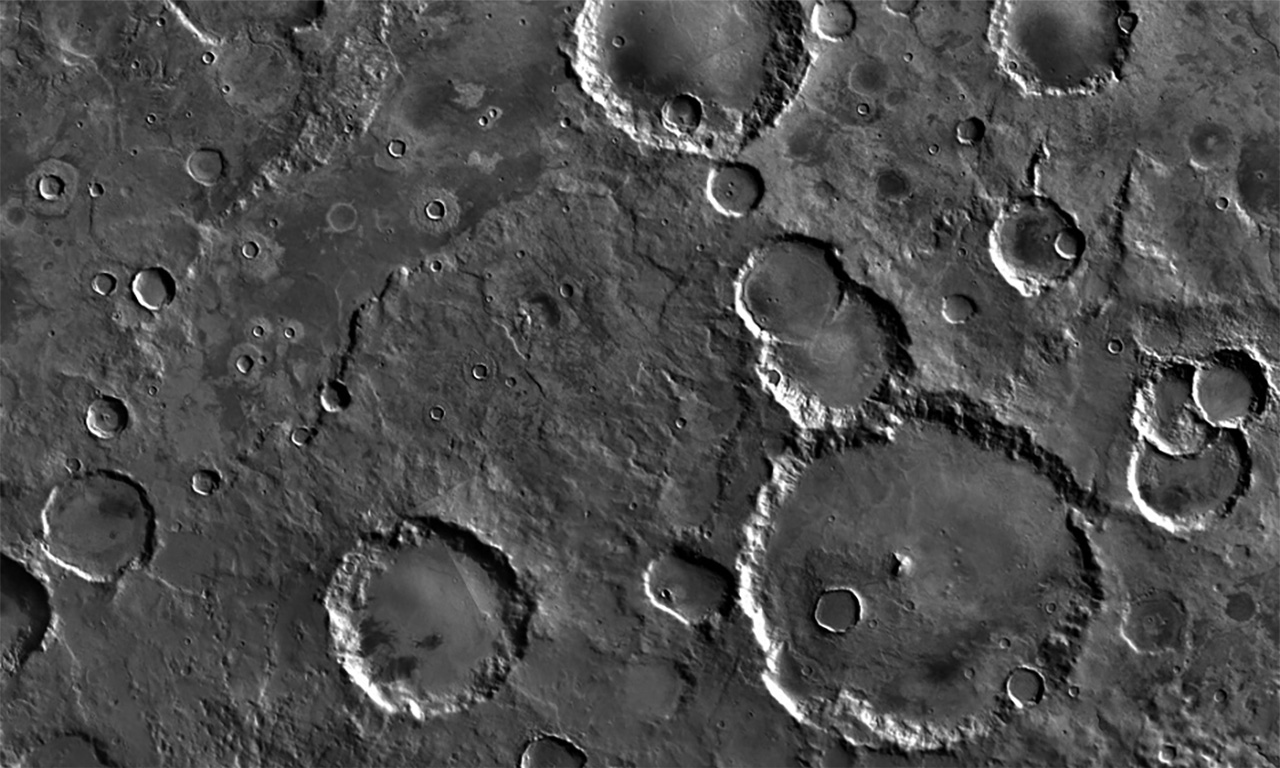
Impact craters are the most common geological feature on Mars. Impact craters are roughly circular, excavated holes that are created when a meteor collides with the surface of a planet. In fact, impact craters can be seen on just about every rocky planet, moon and asteroid in our Solar System.
Impact Craters on Mars
Researchers have estimated that Mars is bombarded by more than 200 small asteroids or bits of comets every year forming impact craters at least 12.8 feet (3.9 meters) across. This estimate is calculated based on the number of impact craters found in a systematic survey of a portion of Mars.
After analysing before and after pictures of Martian terrain, researchers of the UA-led HiRISE imaging experiment have identified 248 new impact craters on the red planet. Images were taken using the HiRISE camera onboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. [1]
Largest Impact Craters on Mars
The Hellas Planitia impact crater is located in the southern hemisphere of Mars. This impact basin is roughly 2,300 kilometres (1,400 miles) in diameter and 9 kilometres (5 miles) deep.
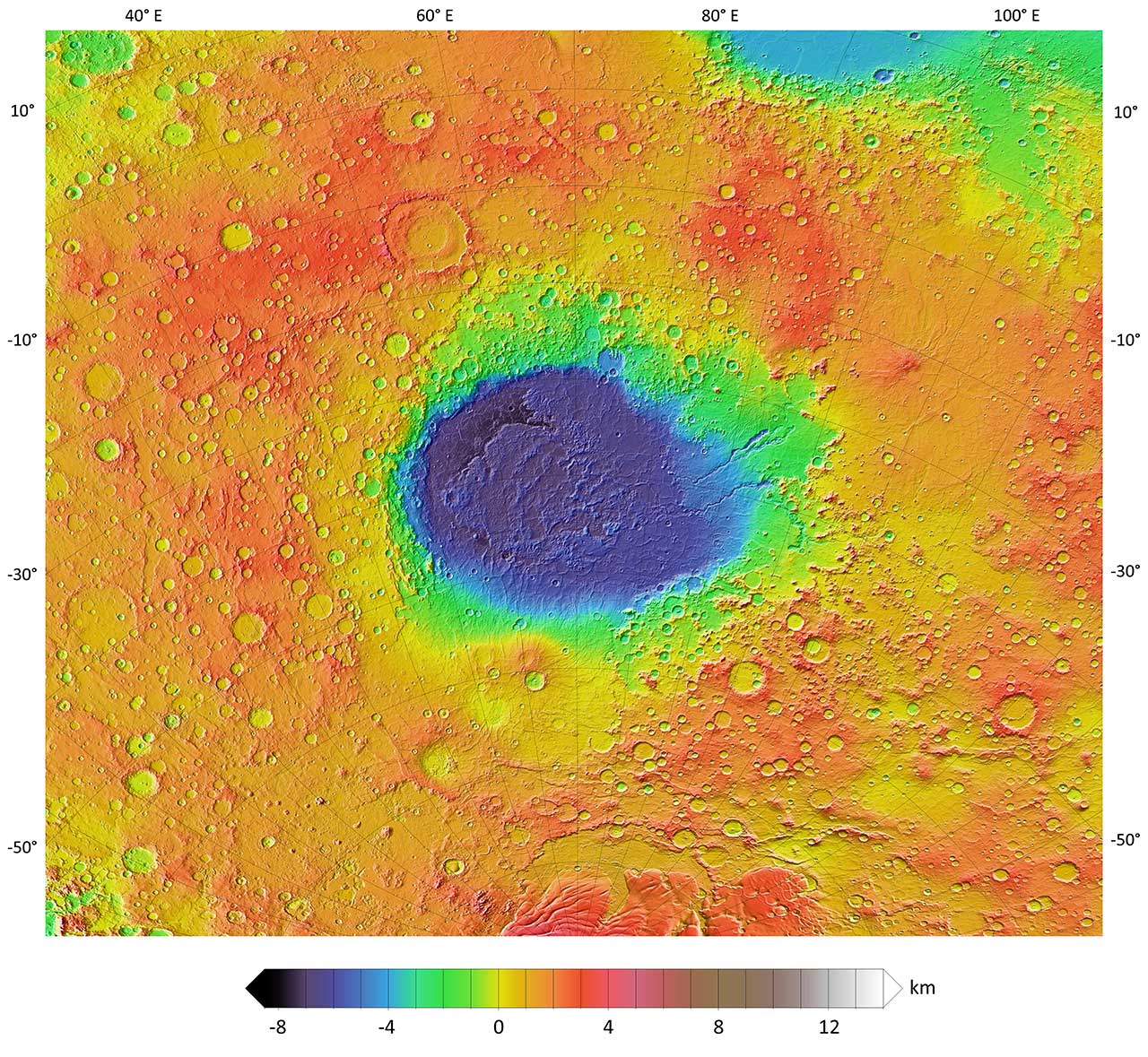
Utopia Planitia is the largest confirmed impact crater on Mars and in the entire Solar System with an estimated diameter of 3300 kilometres (2,100 miles).
Mars Crater Database
University of Colorado Boulder research team has catalogued 635,000 impact craters on Mars that are roughly a kilometre (0.6 miles) or more in diameter. It is the largest single database ever compiled of impact craters on a planet or a moon in our solar system. The Global Mars Crater Database will help in dating the age and geology of particular regions of Mars. [2]
The research on the subject by Stuart Robbins and University of Colorado Boulder faculty member Brian Hynek was published in June 2012 in the Journal of Geophysical Research – Planets, a publication of the American Geophysical Union. [3]
Why Study Impact Craters on Mars?
Mars has a stable crust, low erosion rate and no active lava sources. So impact craters on Mars are not obliterated as they are on Earth. Using the size of an impact crater we can determine the mass and velocity of the meteor that collided there.
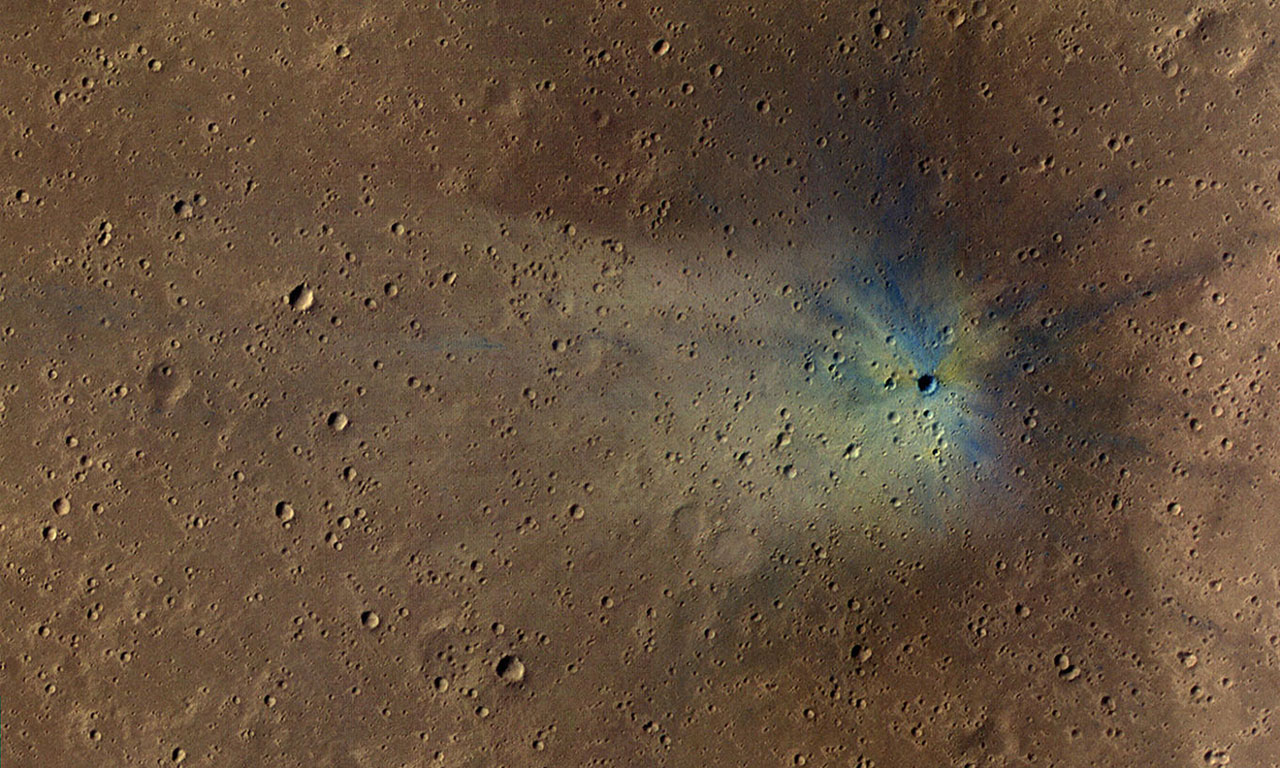
Impact craters are like windows that allow us to look into the past and present of Mars. Scientists record the size and number of impact craters and how eroded they are. Using that information they will determine the age and geological history of Mars.
Footnotes
1. NASA Probe Counts Space Rock Impacts on Mars.
2. Impact atlas catalogs over 635,000 Martian craters.
3. A new global database of Mars impact craters ≥1 km.
4. HiRISE | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment.
